Figure 1 from Regulation of homologous recombination in eukaryotes Biology Diagrams Learn about homologous recombination, the exchange of genetic material between two strands of DNA that contain long stretches of similar base sequences. Find out how it occurs naturally and in genetic engineering, and its role in DNA repair, meiosis, and evolution. machinery, and recombination of a damaged DNA with its sister chromatid re-establishes the DNA replication fork3. Meiotic recombination is 100-1,000-fold more fre-quent than mitotic recombination, and it usually involves homologous chromosomes and generates chromosome-arm crossovers. These crossovers are essential for proper

Learn the definition and narration of homologous recombination, a type of genetic recombination that occurs during meiosis. Find out how it contributes to the genetic variation among offspring.

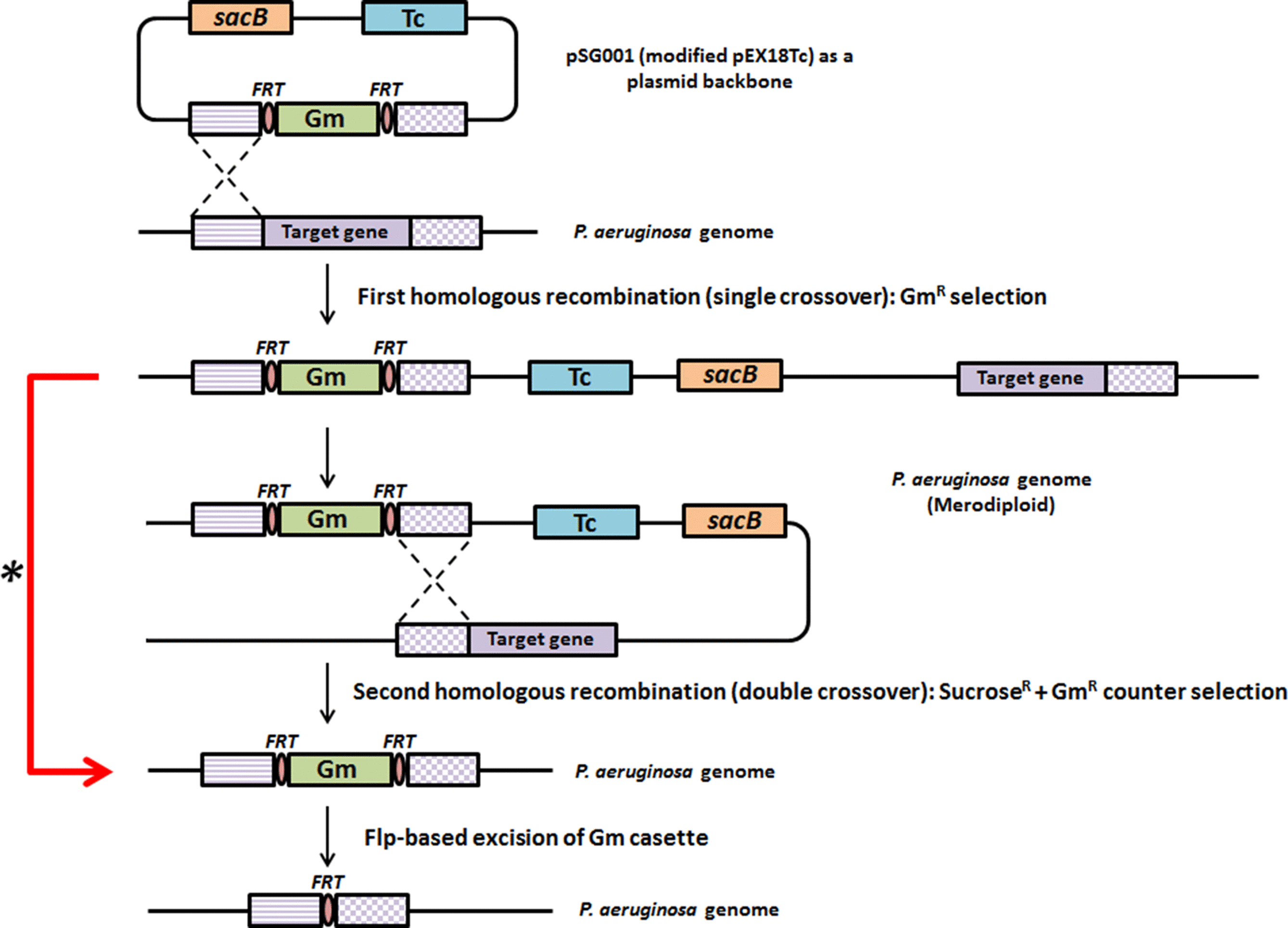
Recombination Between Homologous DNA Sequences Biology Diagrams
Homologous recombination (HR) is an important mechanism for the repair of damaged chromosomes, for preventing the demise of damaged replication forks, and for several other aspects of chromosome
Learn about homologous recombination, a type of genetic recombination that exchanges DNA between similar or identical molecules. Find out how it works, why it is important, and how it is used in gene targeting and evolution.
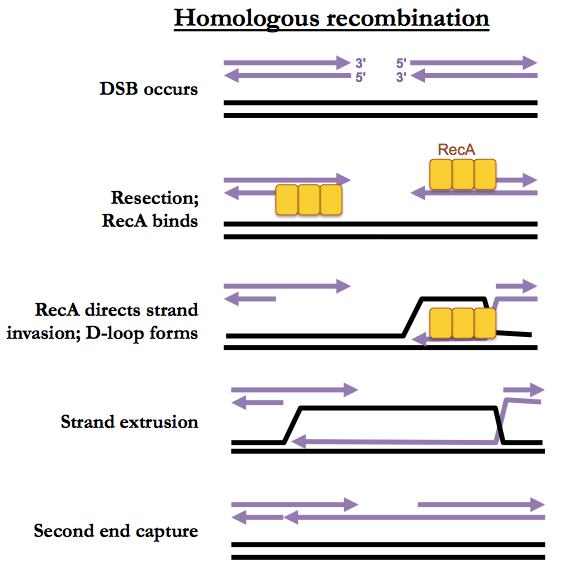
Mechanism of homologous recombination: mediators and helicases ... Biology Diagrams
Homologous recombination (HR) comprises a series of interrelated pathways that function in the repair of DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs) and interstrand crosslinks (ICLs). In addition